Design thinking and innovation are two interrelated concepts that have gained prominence in various fields, particularly in business and product development. Here's an overview of both concepts:
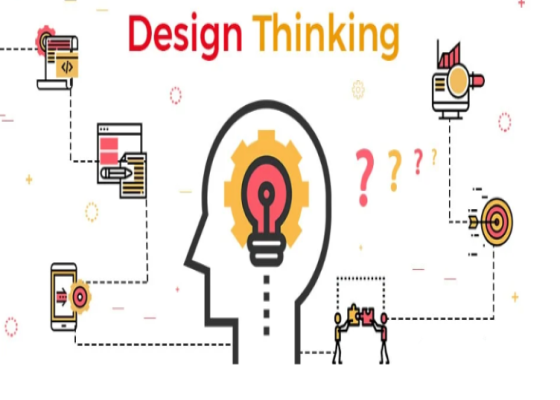
Design Thinking: Design thinking is a human-centered problem-solving approach that focuses on understanding the needs and perspectives of end-users to create innovative and effective solutions. It involves a structured process that typically consists of the following stages:
-
Empathize: Understanding the problem by empathizing with the users. This involves conducting interviews, surveys, and observations to gain insights into their experiences and challenges.
-
Define: Defining the problem based on the insights gathered during the empathize stage. This step helps in framing the problem in a way that can guide the design process.
-
Ideate: Brainstorming and generating creative ideas to address the defined problem. During this stage, teams aim to think beyond conventional solutions and explore a wide range of possibilities.
-
Prototype: Creating tangible representations of potential solutions. Prototypes can be sketches, physical models, or digital mock-ups. Prototyping allows for quick testing and refinement of ideas.
-
Test: Gathering feedback from users by testing the prototypes. This step helps in evaluating the viability and effectiveness of the proposed solutions. Iteration may occur based on user feedback.
Design thinking is often characterized by its iterative and user-centric nature. It encourages teams to approach problems with empathy, creativity, and a willingness to experiment, ultimately leading to innovative and user-friendly solutions.
Innovation: Innovation is the process of developing and implementing new ideas, products, processes, or services that bring value to individuals, organizations, or society. Innovation can manifest in various forms, including technological advancements, business models, or creative solutions to existing problems.
Key aspects of innovation include:
-
Creativity: Innovation often starts with creative thinking, where individuals or teams generate novel ideas and concepts.
-
Problem Solving: Innovation aims to address specific challenges or seize opportunities, making it closely related to problem-solving.
-
Execution: Transforming ideas into tangible outcomes is a crucial aspect of innovation. This can involve research, development, testing, and implementation.
-
Market Impact: Successful innovation has a positive impact on markets, industries, and society by providing unique and valuable solutions.
-
Continuous Improvement: Innovation is an ongoing process that requires organizations to adapt, evolve, and continuously seek improvement.
In summary, design thinking and innovation are complementary concepts. Design thinking provides a structured approach for problem-solving and idea generation, while innovation encompasses the broader process of bringing new and valuable ideas to fruition. Both are essential for organizations and individuals seeking to stay competitive and make a positive impact in today's dynamic world.